In the IELTS Writing section, understanding the difference between Formal language and Informal language is crucial. If candidates cannot distinguish between these two types of language, their writing may inadvertently become inappropriate for the context or lack academic quality, leading to unnecessary point deductions.
In this article, IDP will help you grasp the knowledge of what Formal and Informal are when considering the aspects of vocabulary, writing style, how to distinguish between formal and informal, as well as the stylistic errors you need to avoid during the IELTS Writing test.
1. Definition of Formal and Informal Language
1.1 What is Formal Language?
Formal language is used in written texts, primarily in academic and professional contexts. Types of information that typically use formal language include contracts, essays, reports, and other similar documents.
In addition to written style, you will encounter situations where formal language is necessary, such as presentations, speeches, lectures, ceremonies, conferences, high-level meetings, or communication with older people, superiors, and partners to demonstrate professionalism and respect.
1.2 What is Informal Language?
Informal language is non-formal language, typically used in everyday communication or when writing to close acquaintances. People often use informal language to express a friendly attitude when communicating or writing to family members, friends, and familiar individuals.
2. When should Formal and Informal Language be used?
Formal and Informal language have completely different rules for vocabulary usage and grammar.
For the Academic Writing skill of the IELTS test, candidates must complete all Tasks in the exam and apply Formal Language.
When choosing the IELTS General test format, candidates only need to apply Formal language for Task 2. Task 1 can be presented in formal, semi-formal, or informal form depending on the requirements of the question.
Therefore, you need to understand clearly how to use formal and informal language to apply it fluently and accurately, avoiding losing points in the exam.
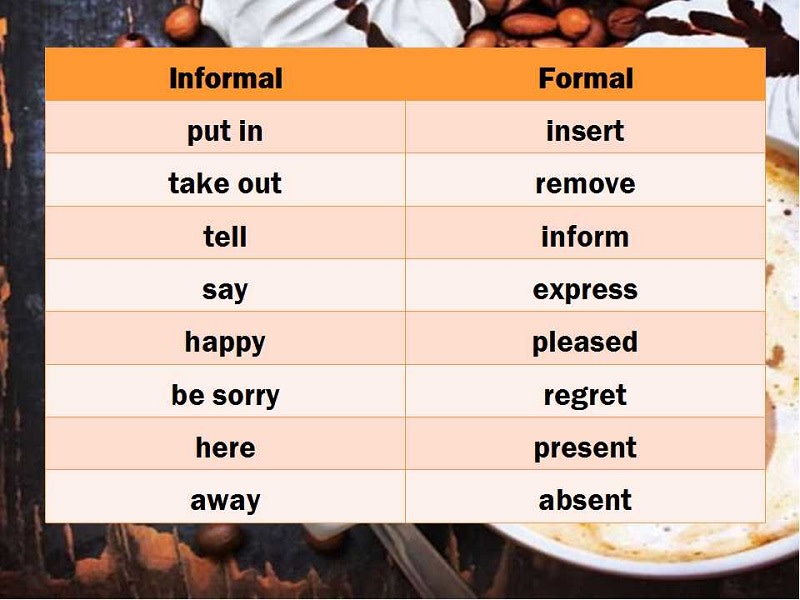
Some examples of Formal and Informal Language in IELTS Writing
3. Cách áp dụng Formal Language trong IELTS Writing
3.1 Formal Language Vocabulary in IELTS Writing
Many candidates often mistakenly believe that to achieve a high score, essays using formal language need to employ new and complex vocabulary. In reality, vocabulary in the formal language group should only tend to be slightly more advanced and complex, avoiding the use of difficult words from dictionaries in the essay.
To apply formal language correctly, you need to use words accurately in each context. Unless the words you use are unacceptable or contain errors, you will still receive points if used correctly.
Consider the following two sentences:
Over the past fifty years, human beings have cut down more than half of the world's trees.
Over the past fifty years, human beings have deforestation more than half of the world's trees.
(Over the past 50 years, humans have cut down more than half of the world's trees)
Although expressing the same content, these two sentences use different phrases: "cut down" and "deforestation" to describe the action of cutting trees. The word "deforestation" is considered more formal language than "cut down trees". However, the correct answer that doesn't lose points is the sentence above because it is grammatically correct. The word "deforestation" is a noun referring to forest destruction, used in the sentence below in the position of a verb, which is incorrect.
3.2 Formal Language Grammar in IELTS Writing
For IELTS Academic Writing, notable grammatical elements in the Formal Language group include:
Passive Voices
Passive voices are commonly applied in Formal Language as they provide a more objective view and remove personal elements from the sentence. In some professional conversations and formal discussions, using passive voice will help you present ideas better. However, be careful to apply it in the right context and not overuse this sentence form.
Example:
Developers launched Google Translate in 2006. (Active voice)
→ Google Translate was launched in 2006. (Passive voice)
Participle Clauses
Participle clauses are an important aspect when applying Formal Language in IELTS Writing. Using this grammatical element will make your writing more logical and coherent, while demonstrating your ability to use grammar flexibly.
Nominalisation
Nominalisation is the process of converting a verb or adjective into a noun or noun phrase without changing their meaning. When applying this grammatical form, personal pronouns will be used less to make the writing more objective and professional.
Example:
Governments want to improve education standards
→ Governments want to make an improvement in education standards
Hedging Language
To score points on the Task Response criterion, you can apply Hedging language. This is cautious language aimed at preventing writers from absolutizing issues without accurate supporting information. However, these languages still ensure the generality of the argument.
Hedging language includes:
Frequency adverbs: never, scarcely ever, hardly ever
Quantifiers: few, a minority of, most, all/every/each,…
Modal verbs: might, could, should, ought to, have to..
Adverbs of certainty: unlikely, perhaps, possibly…
Example:
Based on this passage, Mr. Woolwick probably doesn't like to be disturbed while in bed.
→ Based on this passage, Mr. Woolwick values his privacy while in his bedchambers
4. How to Apply Informal Language in IELTS Writing
Informal language includes omissions, word abbreviations, and flexible, creative word usage in presentations. For IELTS Academic, you should avoid informal writing. However, for IELTS General Training, you can apply informal language in letter writing tasks.
Informal language includes the use of slang, personal pronouns, idioms, and sometimes writers can break grammatical rules in sentences.
Informal language | Explanation | Example |
Slangs | Words that are not formal and do not conform to standard language usage. | I want to know if you're down to hit the cinema this weekend. |
Personal pronouns (first and second person) | "I", "We", "You" | You're one step ahead of me. |
Contractions | Shortened words or combining two words into one. | They're going to give us their old furniture. Isn't that nice? |
Idioms | Fixed phrases that carry meanings different from their literal components. | I like to let my hair down on the dance floor. |
5. Common informal language mistakes to avoid in IELTS Writing

Making too many mistakes related to Informal Language can cause you to lose unnecessary points in the IELTS exam.
5.1 Using contractions, abbreviations, slang
Contractions (I'd, It's) or slang will make your writing less formal. Therefore, avoid using contractions and instead use words typically applied in Formal Language.
Example:
Informal: I donʼt believe that the results are accurate.
Formal: The results are not believed to be accurate.
5.2 Using Clichés (overused, stereotypical phrases)
Clichés are often used in daily communication or artistic creation to make the conveyed information more prominent. However, you should limit their use in Academic Writing, especially when you are presenting work applying Formal Language.
Example:
Every coin has two sides/ Everything has two sides
→ There are two sides to every argument.
5.3 Using too many questions in the essay
One of the scoring criteria for the IELTS Writing test is Task Response, which requires candidates to answer the question's focus correctly. Therefore, using too many questions in the essay will cause the writing to deviate from the main focus and gradually become off-topic.
Example:
But will this strategy work?
→ It is doubtful whether this strategy will succeed.
5.4 Using emotive language
For the IELTS Academic test, all academic language must maintain objectivity, neutrality, and scientific nature. Therefore, you need to avoid using styles and vocabulary that express emotions in your essay.
Example: "Murderer" is a biased term. Instead, you should choose more legal and neutral terms. For example: violent criminal.
Some people have a habit of using flowery words to make their writing more creative, however, flowery words do not belong to the Informal Language group and will make your essay lose its formality. Limit the use of words such as: amazing, fascinating, wondrous, wonderful, shocking, unbelievable, incredible.
You also need to avoid words that express non-neutral judgments such as good, bad, terrible, ridiculous. You can replace these vocabularies with more objective words, typically such as:
Terrible = dreadful, disastrous, unpleasant, desperate
Wrong = unethical, unfair, irresponsible, corrupt, unprincipled, fraudulent
Ridiculous = impossible, incredible
5.5 Using first and second person pronouns
Although all tasks in the IELTS Writing test will require you to write in a Formal style, this does not mean that you cannot use first and second person pronouns. However, you should limit their use to ensure the formality of your writing, only using first and second person pronouns when necessary.
Examples:
In my opinion
I firmly believe that…
I would argue that…
I am of the opinion that…
I side with those who argue that…
6. Exercise on distinguishing between Formal and Informal language
Exercise 1: Choose the answer written in Formal Language
1. Which phrase expresses formal enthusiasm?
A. You're so lucky.
B. I would just like to say how pleased I am for you.
C. That's fantastic! Well done!
2. Which phrase is for giving instructions in a formal way?
A. Now make a plan.
B. The first step would be to make a plan.
C. First you need to make a plan.
3. Which phrase is a formal suggestion?
A. I recommend having lunch in this Chinese restaurant.
B. We are having lunch in this Chinese restaurant.
C. Let's have lunch in this Chinese restaurant!
4. Which phrase expresses thanks in an informal way?
A. I would like to express my sincerest gratitude.
B. You shouldn't have bothered.
C. Thanks a lot. I'm much obliged.
5. Which phrase is an informal request for information?
A. Can you send me a copy by email attachment, please?
B. Send it to me immediately by attachment.
C. I would really appreciate it if you could send me a copy by email attachment.
6. Which phrase is for expressing a preference in a formal way?
A. I'm not doing that.
B. I would rather not do that.
C. I don't want to do that.
7. Which phrase is a formal apology?
A. I would just like to apologize for forgetting your birthday.
B. Look, I just forgot, okay.
C. I'm really sorry I forgot your birthday.
Answers
1. B
2. B
3. A
4. C
5. A
6. B
7. A
We hope that with the information provided above, you have gained a clear understanding of what Formal and Informal Language are, as well as the differences between them. Using the correct language style in IELTS not only helps you avoid unnecessary mistakes but also makes it easier to score high in the IELTS Writing section.
7. Prepare for the IELTS Writing test with IDP!
Dedicating time to practice for the IELTS Writing test early on is one of the key factors for success, especially if you are improving your writing skills and practicing methods to use vocabulary and grammar flexibly in your essays.
In addition to knowledge about Formal and Informal Language, you should also learn other grammar concepts. Early preparation will help you become familiar with the test structure, as well as gain confidence on the test day and achieve the score you desire!
Don't forget to take time to review IDP's available IELTS resources for better preparation. The materials provided include IELTS workshops and events, Test preparation courses and tips from international IELTS experts!
And when you're ready, register for IELTS with IDP today!
